Africa is the only continent in the world that lies across the centre of the Earth. This position is marked by the Equator, an imaginary line that runs horizontally around the globe at 0° latitude.
African countries on the Equator are countries that the Equator passes through or closely touches.
What Is the Equator?

Think of the Earth like an orange. If you slice it straight across the middle, that line you cut along? That’s basically the Equator. It’s the point where the Earth gets the most direct sunlight all year round.
Because of this, countries on the Equator receive nearly all the sunlight, and that has a direct impact on their weather and environment.
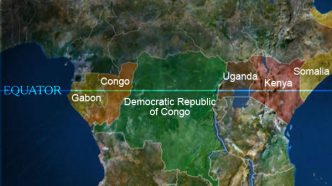
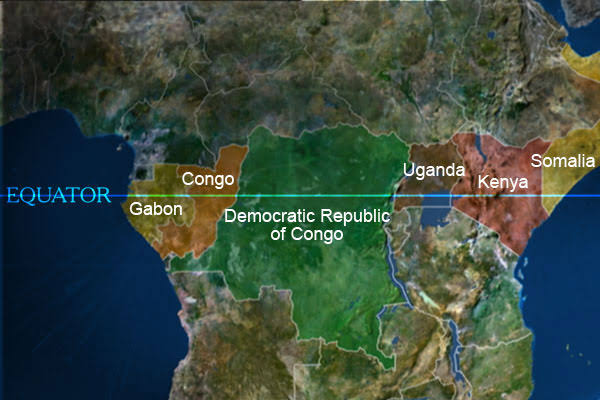
African Countries Located on the Equator
Only seven African countries are located on the Equator, and they are: Uganda Somalia Kenya Gabon, Congo, DR Congo São Tomé & Príncipe.
These countries are located in the east and central parts of Africa.
What Being on the Equator Means for Climate
One of the biggest effects of being on the Equator is climate. African countries on the Equator experience warm temperatures all year round. Very little difference between day and night length, high humidity, as well as heavy rainfall.
Instead of the four seasons common in North and South African regions, these countries usually have wet and dry seasons, just like the West African region.
This climate supports dense rainforests, fertile soils, and a wide variety of plant and animal life.
ALSO READ: Do You Know Your Demonyms? What People From Every African Country Are Called
What Impact Does it Have on Vegetation and Wildlife?
Because of the constant warmth and rainfall, equatorial Africa is home to some of the world’s richest ecosystems. The Congo Basin rainforest, for example, is the world’s second largest tropical rainforest on Earth and plays a crucial role in regulating the global climate.
The environment of countries on the Equator offers diverse wildlife for primates, forest elephants, and countless bird and insect species.
Why Does the Equator Matter?
Knowing which African countries are on the Equator actually explains a lot. From how people farm and what foods they grow to the kind of wildlife you will find and even how daily life goes on.
That single line you see on the map shapes the climate, the crops, and the rhythm of life in these places.
Think of it this way: African countries on the Equator sit right at the Earth’s centre. Because of this position, they enjoy warmth, fertile land, and rich natural resources like oil and gas deposits (especially in Gabon and the Republic of the Congo) and precious minerals such as diamonds, gold, and coltan, particularly in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
So next time you’re looking at a map of Africa and you see that straight line running across it, remember that those countries along that line are equatorial African countries.
Places that receive direct sunlight and where even things like shadows behave a little differently. That one line explains a lot about their climate and way of life.